Part 4
This was created by Joni Virtanen
The goal
Setting up the host.
As usual, you will need to harden the host system.
- Create firewall rules
- Enable fail2ban
- Anything else?
To run Docker images you will need to install the Docker Engine. Follow the instructions (Ubuntu).
You might also want to install Docker-Compose. It is not necessary, but highly recommended. If you decide to take the hard path and go without docker-compose you will need to skim through the next part and launch the services manually.
Docker-Compose
Rocket.chat github provides us with a template. Docker-compose file-reference could prove useful.
Rocket.Chat docker-compose.yml contains multiple named services and their required parameters, mount paths etc.
You should be able to run this compose file with docker-compose -d up. It will run the containers in a specified order based on the depends_on attributes.
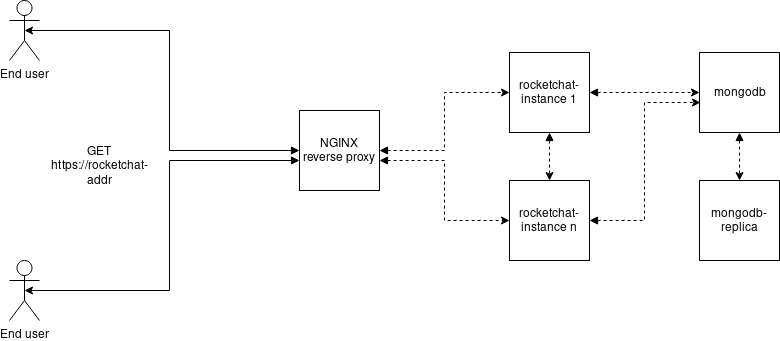
This will leave us in the following situation.

SSL certificates
Services on the interenet should be communicating with end users using encryption whenever they need to gather personal data or credentials from an user. We would be using commercial certificates to prove our services identity if we could. This does not necessarily translate to increases in production costs, since there are services like Let’s Encrypt available. However it is not possible in our virtual environment to use this kind of approach, so we will be doing it using Self-Signed Certificates.
Self-Signed Certificates work just as well, as long as you can trust the certificate. The negative side is that there is no one to publicly announce:
Hey, this domain name holds a certificate “certificate” and the one served to you seems to match it! You can trust this service!
We can generate our own certificate using OpenSSL software. For this material, you may want to create the certificate on the host. If you create the certificate inside the container, you will have to adapt your system accordingly.
openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /etc/nginx/certificate.key -out /etc/nginx/certificate.crt
Parameter breakdown:
- req - PKCS#10 certificate request and certificate generating utility.
- x509 - this option outputs a self signed certificate instead of a certificate request.
- nodes - if this option is specified then if a private key is created it will not be encrypted.
- newkey - this option creates a new certificate request and a new private key.
- keyout - this gives the filename to write the newly created private key to.
- out - This specifies the output filename to write to or standard output by default.
modify it to meet your own needs. It might help you if you saved these files to some specific directory in an organized way.
Check the permissions for the certificates private key. Who should be able to do what with it? Do the same thing for the public key.
Diffie-Hellman Algorithm Generate it.
openssl dhparam 2048 -out <polku>/dhparam.pem
NGINX
We will use NGINX as a reverse proxy for our service. It’s not absolutely necessary yet, but it it will be crucial later in this project.
To configure NGINX create a configuration file whatever.conf. Yet again for the sake of your own mind, just save it somewhere you can remember.
Example documentation. Note all the other examples listed on the site. Admin Guide. nginx.conf
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name localhost;
error_log /var/log/nginx/rocketchat_error.log;
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/certificate.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/certificate.key;
ssl_dhparam /etc/nginx/dhparams.pem;
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2;
ssl_ciphers 'ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:DHE-DSS-AES128-GCM-SHA256:kEDH+AESGCM:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA:DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA:DHE-DSS-AES128-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA256:DHE-DSS-AES256-SHA:DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA:AES128-GCM-SHA256:AES256-GCM-SHA384:AES128-SHA256:AES256-SHA256:AES128-SHA:AES256-SHA:AES:CAMELLIA:DES-CBC3-SHA:!aNULL:!eNULL:!EXPORT:!DES:!RC4:!MD5:!PSK:!aECDH:!EDH-DSS-DES-CBC3-SHA:!EDH-RSA-DES-CBC3-SHA:!KRB5-DES-CBC3-SHA';
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:20m;
ssl_session_timeout 180m;
location / {
proxy_pass http://rocketchat:3000;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forward-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forward-Proto http;
proxy_set_header X-Nginx-Proxy true;
proxy_redirect off;
}
}
Previous snippet will enable your server to listen on port 443 for connections. It will also determine where NGINX will write it’s error logs. On top of this it has lots of arguments for SSL connection, including your certification path. More information can be found at NGINX documentation. It also specifies a proxy pass for location “/”. This means that all the requests ending in “https://rooturl/” will be redirected to the address specified in proxy_pass attribute. More information can be found here.
NGINX documentation contains more information.
Now we will need to create a service for it.
services:
nginx:
image: nginx
volumes:
- <config mount>
- <certificates mount>
ports:
- "443:443"
depends_on:
- rocketchat
if we run docker-compose up -d now, we will have following situation:

Scaling
We can scale the service similarly as in the exercise 2.5. Do that. Now we need to tell nginx that we want it to distribute the incoming connections between the rocket.chat containers.
Modify the NGINX configuration file like so:
upstream rocket {
server rocketchat:3000;
}
server {
...
location / {
proxy_pass http://rocket/;
...
}
}
Make sure it works. You can pause containers using docker pause <container>.